Collect telemetry for MCP workloads
In this tutorial, you'll set up comprehensive observability for your MCP workloads using OpenTelemetry with Jaeger for distributed tracing, Prometheus for metrics collection, and Grafana for visualization.
By the end, you'll have a complete, industry-standard observability solution that captures detailed traces and metrics, giving you visibility into your MCP server performance and usage patterns.
Choose your deployment path
This tutorial offers two paths for MCP observability:
- ToolHive CLI
- Kubernetes Operator
ToolHive CLI + Docker observability stack
Use the ToolHive CLI to run MCP servers locally, with Jaeger and Prometheus running in Docker containers. This approach is perfect for:
- Local development and testing
- Quick setup and experimentation
- Individual developer workflows
- Learning OpenTelemetry concepts
ToolHive Kubernetes Operator + in-cluster observability
Use the ToolHive Kubernetes operator to manage MCP servers in a cluster, with Jaeger and Prometheus deployed inside Kubernetes. This approach is ideal for:
- Production-like environments
- Team collaboration and shared infrastructure
- Container orchestration workflows
- Scalable observability deployments
Select your preferred deployment method using the tabs above. All subsequent steps will show instructions for your chosen path.
What you'll learn
- How to deploy Jaeger and Prometheus for your chosen environment
- How to configure OpenTelemetry collection for ToolHive MCP servers
- How to analyze traces in Jaeger and metrics in Prometheus
- How to set up queries and monitoring for MCP workloads
- Best practices for observability in your deployment environment
Prerequisites
Before starting this tutorial, make sure you have:
- ToolHive CLI
- Kubernetes Operator
- Completed the ToolHive CLI quickstart
- A supported container runtime installed and running. Docker or Podman are recommended for this tutorial
- Docker Compose or Podman Compose available
- A supported MCP client for testing
- Completed the ToolHive Kubernetes quickstart with a local kind cluster
kubectlconfigured to access your cluster- Helm (v3.10 minimum) installed
- A supported MCP client for testing
- The ToolHive CLI (optional, for client configuration)
- Basic familiarity with Kubernetes concepts
Overview
The architecture for each deployment method:
- ToolHive CLI
- Kubernetes Operator
Your setup will include:
- ToolHive CLI managing MCP servers in containers
- Jaeger for distributed tracing with built-in UI
- Prometheus for metrics collection with web UI
- OpenTelemetry Collector forwarding data to both backends
Your setup will include:
- ToolHive Operator managing MCP servers as Kubernetes pods
- Jaeger for distributed tracing
- Prometheus for metrics collection
- Grafana for metrics visualization
- OpenTelemetry Collector running as a Kubernetes service
Step 1: Deploy the observability stack
First, set up the observability infrastructure for your chosen environment.
- ToolHive CLI
- Kubernetes Operator
Create Docker Compose configuration
Create a Docker Compose file for the observability stack:
services:
jaeger:
image: jaegertracing/jaeger:latest
container_name: jaeger
environment:
- COLLECTOR_OTLP_ENABLED=true
ports:
- '16686:16686' # Jaeger UI
networks:
- observability
prometheus:
image: prom/prometheus:latest
container_name: prometheus
command:
- '--config.file=/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml'
- '--storage.tsdb.path=/prometheus'
- '--web.console.libraries=/etc/prometheus/console_libraries'
- '--web.console.templates=/etc/prometheus/consoles'
- '--web.enable-lifecycle'
- '--enable-feature=native-histograms'
ports:
- '9090:9090'
volumes:
- ./prometheus.yml:/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml
- prometheus-data:/prometheus
networks:
- observability
grafana:
image: grafana/grafana:latest
container_name: grafana
environment:
- GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_USER=admin
- GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_PASSWORD=admin
- GF_USERS_ALLOW_SIGN_UP=false
ports:
- '3000:3000'
volumes:
- ./grafana-prometheus.yml:/etc/grafana/provisioning/datasources/prometheus.yml
- grafana-data:/var/lib/grafana
networks:
- observability
otel-collector:
image: otel/opentelemetry-collector-contrib:latest
container_name: otel-collector
command: ['--config=/etc/otel-collector-config.yml']
volumes:
- ./otel-collector-config.yml:/etc/otel-collector-config.yml
ports:
- '4318:4318' # OTLP HTTP receiver (ToolHive sends here)
- '8889:8889' # Prometheus exporter metrics
depends_on:
- jaeger
- prometheus
networks:
- observability
volumes:
prometheus-data:
grafana-data:
networks:
observability:
driver: bridge
Configure the OpenTelemetry Collector
Create the collector configuration to export to both Jaeger and Prometheus:
receivers:
otlp:
protocols:
http:
endpoint: 0.0.0.0:4318
processors:
batch:
timeout: 10s
send_batch_size: 1024
exporters:
# Export traces to Jaeger
otlp/jaeger:
endpoint: jaeger:4317
tls:
insecure: true
# Expose metrics for Prometheus
prometheus:
endpoint: 0.0.0.0:8889
const_labels:
service: 'toolhive-mcp-proxy'
service:
pipelines:
traces:
receivers: [otlp]
processors: [batch]
exporters: [otlp/jaeger]
metrics:
receivers: [otlp]
processors: [batch]
exporters: [prometheus]
Configure Prometheus and Grafana
Create a Prometheus configuration to scrape the OpenTelemetry Collector:
global:
scrape_interval: 15s
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'otel-collector'
static_configs:
- targets: ['otel-collector:8889']
Create the Prometheus data source configuration for Grafana:
apiVersion: 1
datasources:
- name: prometheus
type: prometheus
access: proxy
url: http://prometheus:9090
isDefault: true
editable: true
Start the observability stack
Deploy the stack and verify it's running:
# Start the stack
docker compose -f observability-stack.yml up -d
# Verify Jaeger is running
curl http://localhost:16686/api/services
# Verify Prometheus is running
curl http://localhost:9090/-/healthy
# Verify the OpenTelemetry Collector is ready
curl -I http://localhost:8889/metrics
Access the interfaces:
- Jaeger UI:
http://localhost:16686 - Prometheus Web UI:
http://localhost:9090 - Grafana:
http://localhost:3000(login: admin/admin)
Prerequisite
If you've completed the Kubernetes quickstart, skip to the next step.
Otherwise, set up a local kind cluster and install the ToolHive operator:
kind create cluster --name toolhive
helm upgrade -i toolhive-operator-crds oci://ghcr.io/stacklok/toolhive/toolhive-operator-crds
helm upgrade -i toolhive-operator oci://ghcr.io/stacklok/toolhive/toolhive-operator -n toolhive-system --create-namespace
Verify the operator is running:
kubectl get pods -n toolhive-system
Create the monitoring namespace
Create a dedicated namespace for your observability stack:
kubectl create namespace monitoring
Deploy Jaeger
Install Jaeger using Helm with a configuration suited for ToolHive:
helm repo add jaegertracing https://jaegertracing.github.io/helm-charts
helm repo update
helm upgrade -i jaeger-all-in-one jaegertracing/jaeger -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stacklok/toolhive/refs/tags/v0.3.6/examples/otel/jaeger-values.yaml -n monitoring
Deploy Prometheus and Grafana
Install Prometheus and Grafana using the kube-prometheus-stack Helm chart:
helm repo add prometheus-community https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-charts
helm repo update
helm upgrade -i kube-prometheus-stack prometheus-community/kube-prometheus-stack -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stacklok/toolhive/v0.3.6/examples/otel/prometheus-stack-values.yaml -n monitoring
Deploy OpenTelemetry Collector
Create the collector configuration and deployment manifest:
helm repo add open-telemetry https://open-telemetry.github.io/opentelemetry-helm-charts
helm repo update
helm upgrade -i otel-collector open-telemetry/opentelemetry-collector -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stacklok/toolhive/v0.3.6/examples/otel/otel-values.yaml -n monitoring
Verify all components
Verify all components are running:
kubectl get pods -n monitoring
Wait for all pods to be in Running status before proceeding. The output should look similar to:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
jaeger-all-in-one-6bf667c984-p5455 1/1 Running 0 2m12s
kube-prometheus-stack-grafana-69c88f77c5-b9f7m 3/3 Running 0 37s
kube-prometheus-stack-kube-state-metrics-55cb9c8889-cnlkt 1/1 Running 0 37s
kube-prometheus-stack-operator-85655fb7cd-rxms9 1/1 Running 0 37s
kube-prometheus-stack-prometheus-node-exporter-zzcvh 1/1 Running 0 37s
otel-collector-opentelemetry-collector-agent-hqtnq 1/1 Running 0 11s
prometheus-kube-prometheus-stack-prometheus-0 2/2 Running 0 36s
Step 2: Configure MCP server telemetry
Now configure your MCP servers to send telemetry data to the observability stack.
- ToolHive CLI
- Kubernetes Operator
Set global telemetry configuration
Configure ToolHive CLI with default telemetry settings to send data to the OpenTelemetry Collector:
# Configure the OpenTelemetry endpoint (collector, not directly to Jaeger)
thv config otel set-endpoint localhost:4318
# Enable both metrics and tracing
thv config otel set-metrics-enabled true
thv config otel set-tracing-enabled true
# Set 100% sampling for development
thv config otel set-sampling-rate 1.0
# Use insecure connection for local development
thv config otel set-insecure true
Run an MCP server with telemetry
Start an MCP server with enhanced telemetry configuration:
thv run \
--otel-service-name "mcp-fetch-server" \
--otel-env-vars "USER,HOST" \
--otel-enable-prometheus-metrics-path \
fetch
Verify the server started and is exporting telemetry:
# Check server status
thv list
# Check Prometheus metrics are available on the MCP server
PORT=$(thv list | grep fetch | awk '{print $5}')
curl http://localhost:$PORT/metrics
Create an MCP server with telemetry
Create an MCPServer resource with comprehensive telemetry configuration:
apiVersion: toolhive.stacklok.dev/v1alpha1
kind: MCPServer
metadata:
name: fetch-telemetry
namespace: toolhive-system
spec:
image: ghcr.io/stackloklabs/gofetch/server
transport: streamable-http
proxyPort: 8080
mcpPort: 8080
resources:
limits:
cpu: '100m'
memory: '128Mi'
requests:
cpu: '50m'
memory: '64Mi'
telemetry:
openTelemetry:
enabled: true
endpoint: otel-collector-opentelemetry-collector.monitoring.svc.cluster.local:4318
serviceName: mcp-fetch-server
insecure: true # Using HTTP collector endpoint
metrics:
enabled: true
tracing:
enabled: true
samplingRate: '1.0'
prometheus:
enabled: true
Deploy the MCP server:
kubectl apply -f fetch-with-telemetry.yml
Verify the MCP server is running and healthy:
# Verify the server is running
kubectl get mcpserver -n toolhive-system
# Check the pods are healthy
kubectl get pods -n toolhive-system -l app.kubernetes.io/instance=fetch-telemetry
Step 3: Generate telemetry data
Create some MCP interactions to generate traces and metrics for analysis.
- ToolHive CLI
- Kubernetes Operator
Connect your AI client
Your MCP server is already configured to work with your AI client from the CLI quickstart. Simply use your client to make requests that will generate telemetry data.
Port-forward to access the MCP server
In a separate terminal window, create a port-forward to connect your AI client:
kubectl port-forward service/mcp-fetch-telemetry-proxy -n toolhive-system 8080:8080
Leave this running for the duration of this tutorial.
Configure your AI client
Use the ToolHive CLI to add the MCP server to your client configuration:
thv run http://localhost:8080/mcp --name fetch-k8s --transport streamable-http
Generate sample data
Make several requests using your AI client to create diverse telemetry:
- Basic fetch request: "Fetch the content from https://toolhive.dev and summarize it"
- Multiple requests: Make 3-4 more fetch requests with different URLs
- Error generation: Try an invalid URL to generate error traces
Each interaction creates rich telemetry data including:
- Request traces with timing information sent to Jaeger
- Tool call details with sanitized arguments
- Performance metrics sent to Prometheus
The CLI and Kubernetes deployments will both generate similar telemetry data, with the Kubernetes setup including additional Kubernetes-specific attributes.
Step 4: Access and analyze telemetry data
Now examine your telemetry data using Jaeger and Prometheus to understand MCP server performance.
- ToolHive CLI
- Kubernetes Operator
Access Jaeger for traces
Open Jaeger in your browser at http://localhost:16686.
Explore traces in Jaeger
- In the Service dropdown, select
mcp-fetch-server - Click Find Traces to see recent traces
- Click on individual traces to see detailed spans
Look for traces with protocol and MCP-specific attributes like:
{
"serviceName": "mcp-fetch-server",
"http.duration_ms": "307.8",
"http.status_code": 200,
"mcp.method": "tools/call",
"mcp.tool.name": "fetch",
"mcp.tool.arguments": "url=https://toolhive.dev",
"mcp.transport": "streamable-http",
"service.version": "v0.3.6"
}
Access Grafana for visualization
Open http://localhost:3000 in your browser and log in using the default
credentials (admin / admin).
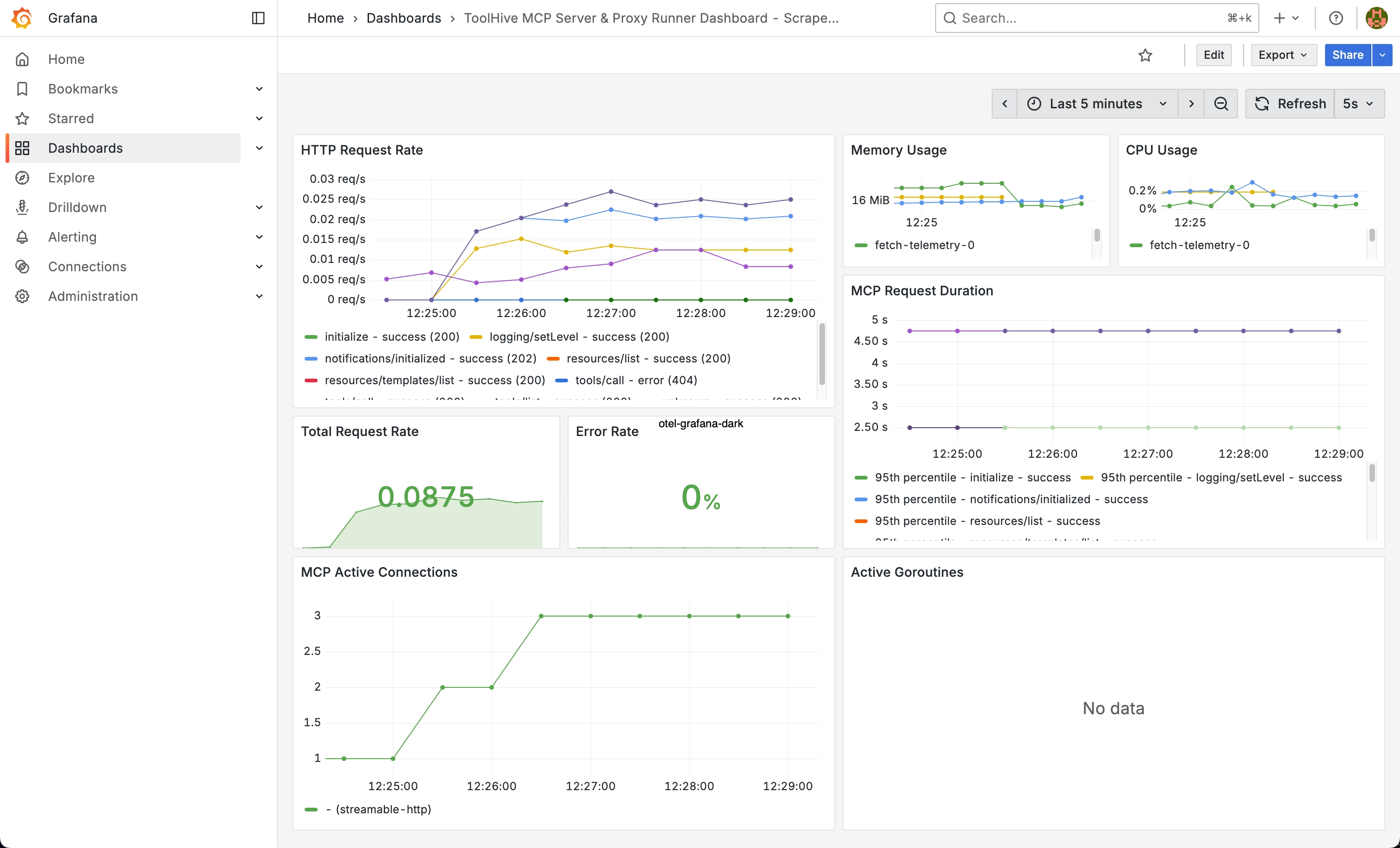
Import the ToolHive dashboard
- Click the + icon in the top-right of the Grafana interface and select Import dashboard
- In the Import via dashboard JSON model input box, paste the contents of this example dashboard file
- Click Load, then Import
Make some requests to your MCP server again and watch the dashboard update in real-time.
You can also explore other metrics in Grafana by creating custom panels and queries. See the Observability guide for examples.
Port-forward to Jaeger
Access Jaeger through a port-forward:
kubectl port-forward service/jaeger-all-in-one-query -n monitoring 16686:16686
Open http://localhost:16686 in your browser.
Explore traces in Jaeger
- In the Service dropdown, select
mcp-fetch-server - Click Find Traces to see recent traces
- Click on individual traces to see detailed spans
Review the available information including MCP and Kubernetes-specific attributes like:
{
"serviceName": "mcp-fetch-server",
"http.duration_ms": "307.8",
"http.status_code": 200,
"mcp.method": "tools/call",
"mcp.tool.name": "fetch",
"mcp.tool.arguments": "url=https://toolhive.dev",
"mcp.transport": "streamable-http",
"k8s.deployment.name": "fetch-telemetry",
"k8s.namespace.name": "toolhive-system",
"k8s.node.name": "toolhive-control-plane",
"k8s.pod.name": "fetch-telemetry-7d7d55687c-glvpz",
"service.namespace": "toolhive-system",
"service.version": "v0.3.6"
}
Port-forward to Grafana
Access Grafana through a port-forward:
kubectl port-forward service/kube-prometheus-stack-grafana -n monitoring 3000:80
Open http://localhost:3000 in your browser and log in using the default
credentials (admin / admin).
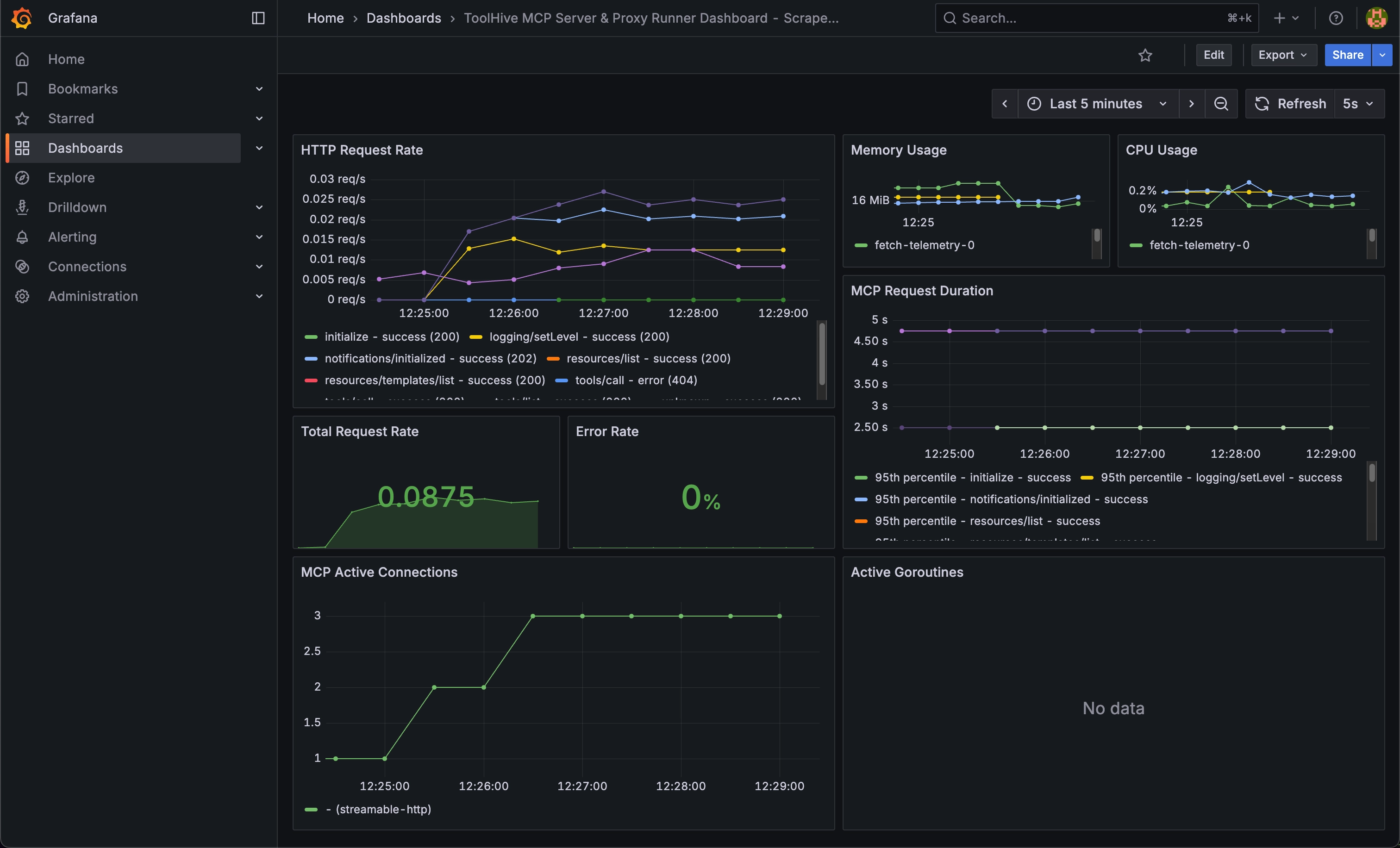
Import the ToolHive dashboard
- Click the + icon in the top-right of the Grafana interface and select Import dashboard
- In the Import via dashboard JSON model input box, paste the contents of this example dashboard file
- Click Load, then Import
Make some requests to your MCP server again and watch the dashboard update in real-time.
You can also explore other metrics in Grafana by creating custom panels and queries. See the Observability guide for examples.
Step 5: Cleanup
When you're finished exploring, clean up your resources.
- ToolHive CLI
- Kubernetes Operator
Stop MCP servers
# Stop and remove the MCP server
thv rm fetch
# Clear telemetry configuration (optional)
thv config otel unset-endpoint
thv config otel unset-metrics-enabled
thv config otel unset-tracing-enabled
thv config otel unset-sampling-rate
thv config otel unset-insecure
Stop observability stack
# Stop all containers
docker compose -f observability-stack.yml down
# Remove all data (optional)
docker compose -f observability-stack.yml down -v
# Clean up provisioning directories (optional)
rm -rf grafana/
Remove MCP servers
# Delete the MCP server
kubectl delete mcpserver fetch-telemetry -n toolhive-system
Remove observability stack
# Delete observability components
helm uninstall otel-collector -n monitoring
helm uninstall kube-prometheus-stack -n monitoring
helm uninstall jaeger-all-in-one -n monitoring
# Remove the monitoring namespace
kubectl delete namespace monitoring
Optional: Remove the kind cluster
If you're completely done:
kind delete cluster --name toolhive
What's next?
Congratulations! You've successfully set up comprehensive observability for ToolHive MCP workloads using Jaeger and Prometheus.
To learn more about ToolHive's telemetry capabilities and best practices, see the Observability concepts guide.
Here are some next steps to explore:
- Custom dashboards: Create Grafana dashboards that query both Jaeger and Prometheus
- Alerting: Set up Prometheus AlertManager for performance and error alerts
- Performance optimization: Use telemetry data to optimize MCP server performance
- Distributed tracing: Understand request flows across multiple MCP servers
- ToolHive CLI
- Kubernetes Operator
CLI-specific next steps
- Review the CLI telemetry guide: Explore detailed configuration options
- Scale to multiple servers: Run multiple MCP servers with different configurations
- Production CLI setup: Learn about secrets management and custom permissions
- Alternative backends: Try other observability platforms mentioned in the CLI telemetry guide
Kubernetes-specific next steps
- Review the Kubernetes telemetry guide: Explore detailed configuration options
- Production deployment: Set up production-grade Jaeger and Prometheus with persistent storage, or configure an OpenTelemetry Collector to work with your existing observability tools
- Advanced MCP configurations: Explore Kubernetes MCP deployment patterns
- Secrets integration: Learn about HashiCorp Vault integration
- Service mesh observability: Integrate with Istio or Linkerd for enhanced tracing
Related information
- Observability concepts - Understanding ToolHive's telemetry architecture
- CLI telemetry guide - Detailed CLI configuration options
- Kubernetes telemetry guide - Kubernetes operator telemetry features
- OpenTelemetry Collector documentation - Official OpenTelemetry Collector documentation
- Jaeger documentation - Official Jaeger documentation
- Prometheus documentation - Official Prometheus documentation
Troubleshooting
- ToolHive CLI
- Kubernetes Operator
Docker containers won't start
Check Docker daemon and container logs:
# Verify Docker is running
docker info
# Check container logs
docker compose -f observability-stack.yml logs jaeger
docker compose -f observability-stack.yml logs prometheus
docker compose -f observability-stack.yml logs otel-collector
Common issues:
- Port conflicts with existing services
- Insufficient Docker memory allocation
- Missing configuration files
ToolHive CLI not sending telemetry
Verify telemetry configuration:
# Check current config
thv config otel get-endpoint
thv config otel get-metrics-enabled
Check the ToolHive proxy logs for telemetry export errors:
thv logs fetch --proxy [--follow]
Alternatively, you can check the log file directly at:
- macOS:
~/Library/Application Support/toolhive/logs/fetch.log - Windows:
%LOCALAPPDATA%\toolhive\logs\fetch.log - Linux:
~/.local/share/toolhive/logs/fetch.log
No traces in Jaeger
Check the telemetry pipeline:
- Verify collector is receiving data:
curl http://localhost:8888/metrics - Check collector logs:
docker logs otel-collector - Verify Jaeger connectivity:
curl http://localhost:16686/api/services
Pods stuck in pending state
Check cluster resources and pod events:
# Check pod status
kubectl get pods -n monitoring
# Describe problematic pods
kubectl describe pod <pod-name> -n monitoring
# Check node resources
kubectl top nodes
Common issues:
- Insufficient cluster resources
- Image pull failures
- Network policies blocking communication
MCP server not sending telemetry
Verify the telemetry configuration and connectivity:
# Check MCPServer status
kubectl describe mcpserver fetch-telemetry -n toolhive-system
# Check OpenTelemetry Collector logs
kubectl logs deployment/otel-collector -n monitoring
# Verify service connectivity
kubectl exec -it deployment/otel-collector -n monitoring -- wget -qO- http://jaeger:16686/api/services
No metrics in Prometheus
Common troubleshooting steps:
- Verify Prometheus targets: Check
http://localhost:9090/targetsto ensureotel-collectortarget is UP - Check collector metrics endpoint:
curl http://localhost:8889/metrics(CLI) or port-forward and check in K8s - Review collector configuration: Ensure the Prometheus exporter is properly configured
- Check Prometheus config: Verify the scrape configuration includes the collector endpoint